Whether you are an athlete, bodybuilder, or fitness enthusiast, you have probably heard of creatine. It is one of the most popular performance-enhancing supplements used by individuals looking to maximize their physical abilities. This article will take a closer look at the science behind creatine and its impact on performance.
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that is found in small amounts in various foods, such as meat and fish. It is also produced by the body in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. Creatine plays a crucial role in energy production, particularly during short bursts of high-intensity activities like weightlifting or sprinting.
How Does Creatine Work?
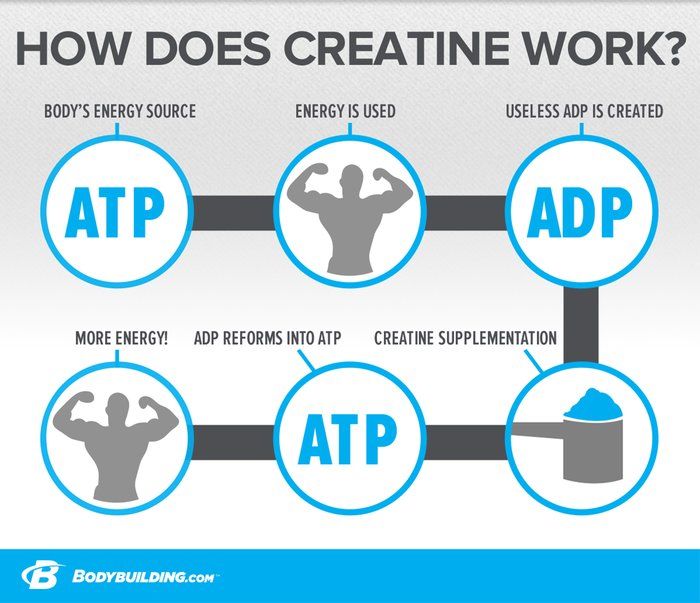
When creatine is consumed, it is converted into phosphocreatine in the body, which then serves as a ready source of energy for the muscles. During intense exercise, the body relies heavily on adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as its primary energy source. However, ATP is quickly depleted, and that’s when phosphocreatine steps in to replenish ATP, allowing the muscles to continue contracting forcefully.
Performance Enhancement
The primary benefit of creatine supplementation is the potential for improved performance in high-intensity, short-duration activities. Various scientific studies have shown that supplementing with creatine can lead to increased power output, enhanced muscular strength, and greater overall performance.
Benefits Beyond Performance
In addition to performance enhancement, creatine has been associated with other benefits. Research suggests that creatine supplementation can increase muscle mass, improve exercise recovery, and reduce muscle damage. It may also have positive effects on brain health and cognitive function, although more research is needed in this area.
Who Can Benefit from Creatine?
Creatine is not only limited to elite athletes or bodybuilders. It can be beneficial to anyone engaging in high-intensity exercise, such as sprinting, jumping, or weightlifting. Individuals looking to gain muscle mass, improve overall strength, or recover faster from intense workouts can also benefit from creatine supplementation.
How to Take Creatine
Creatine is readily available in the form of powder and capsules. The most commonly used form is creatine monohydrate. To load creatine, individuals typically take around 20 grams per day for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day. It is essential to stay adequately hydrated while supplementing with creatine to maximize its effectiveness.
Potential Side Effects
While creatine is generally safe for most individuals, some may experience side effects such as bloating, stomach cramps, or diarrhea. It is crucial to follow recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying medical conditions or concerns.
Conclusion
Creatine is a popular performance booster that has been extensively researched for its benefits on physical performance, muscle mass, and exercise recovery. Whether you are an athlete or a fitness enthusiast, adding creatine to your supplement regimen might help you reach your goals and maximize your potential. However, it is essential to use creatine responsibly and in consultation with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and obtain optimal results.