Electronic Health Records (EHR) have revolutionized the way healthcare providers store, access, and manage patient information. Instead of relying on traditional paper-based records, EHR systems allow for digital storage and retrieval of patient data. This article will explore the benefits and concerns associated with the implementation of EHR systems.
Benefits of Electronic Health Records
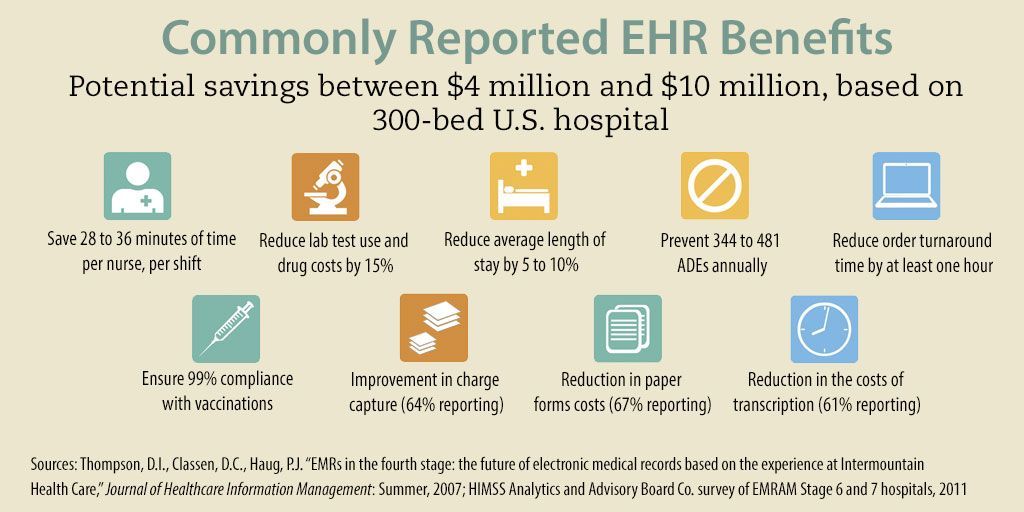
1. Improved Efficiency: EHR systems offer numerous benefits that enhance efficiency within healthcare organizations. Digitized patient records eliminate the need for manual filing, allowing healthcare providers to access patient information instantaneously. This streamlined access to medical records enables faster diagnosis and treatment decisions, saving valuable time in critical situations.
2. Enhanced Coordination: EHR systems facilitate better coordination among healthcare professionals involved in a patient’s care. Multiple providers can access a patient’s complete medical history, reducing the risk of redundant tests or conflicting treatments. Moreover, digital records enable seamless communication and exchange of information across different healthcare settings.
3. Improved Patient Safety: The utilization of EHR systems significantly reduces medical errors. Legible, standardized electronic records minimize misinterpretation of handwritten notes, drug interactions, and allergies. Moreover, EHRs provide real-time alerts and reminders for important screenings, vaccinations, or contraindications, ensuring patients receive appropriate care.
Concerns and Challenges
1. Data Security and Privacy: The digital nature of EHR systems raises concerns about data security and patient privacy. Safeguarding patient records from unauthorized access, hacking, or data breaches is crucial. Healthcare organizations must implement stringent security measures to protect sensitive patient information and comply with privacy regulations, such as HIPAA.
2. Interoperability Issues: Interoperability challenges arise when different healthcare systems struggle to exchange or interpret data seamlessly. Lack of compatibility between systems can hinder the smooth transfer of patient information between healthcare providers, potentially compromising patient care.
3. Cost and Implementation Challenges: Implementing EHR systems can be a complex and expensive process. It requires significant investments in infrastructure, training, and ongoing maintenance. Smaller healthcare providers or rural facilities may struggle with the financial burden associated with implementation, hindering widespread adoption.
Conclusion
While there are concerns and challenges associated with EHR systems, the benefits they offer are substantial. Enhanced efficiency, improved coordination, and increased patient safety are crucial advantages. Addressing concerns related to data security, interoperability, and upfront costs can further bolster the widespread adoption and implementation of EHR systems, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and a more efficient healthcare industry.

